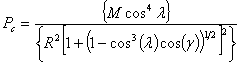B.8
Geomagnetic shielding (Størmer
theory)![]()
At a given location in the field there are minimum cutoff energies necessary for ions to penetrate to that point. Størmer’s theory gives a cutoff rigidity, Pc, for particle arrival at a point, depending on the point’s geomagnetic R, λ coordinates and the angle of ion arrival from east, γ [RN.20].
|
|
(B-13) |
M is the normalized dipole moment of the Earth. From this equation, it can be seen that cosmic rays penetrate the geomagnetic field more easily from the west (γ = 180°) than from the east (γ = 0). The R, λ coordinates can be computed from B and L according to the method of Roberts [RN.28]. For vertical arrival, the expression simplifies to:
|
|
(B-14) |
since γ =90° and R = L cos2 (l)
An approximate value of 16 for the constant M/4 is used to fit with observed effective cutoffs. Magnetospheric disturbances, which often follow solarflares or CMEs, can result in a lowering of cutoff; this has been described by Adams et al. [RN.20] as:
|
|
(B-15) |
with Pc in units of GV.